You are using an unsupported browser. Please upgrade your browser to a newer version to get the best experience on Toxin, Toxin Target Database.
Loxapine (T3D2779)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:26:49 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:51 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D2779 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Loxapine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Loxapine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is an antipsychotic agent used in schizophrenia. Loxapine is a dopamine antagonist, and also a serotonin 5-HT2 blocker. The exact mode of action of Loxapine has not been established, however changes in the level of excitability of subcortical inhibitory areas have been observed in several animal species in association with such manifestations of tranquilization as calming effects and suppression of aggressive behavior. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
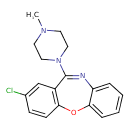
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C18H18ClN3O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 327.808 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 327.114 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 1977-10-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 13-chloro-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxa-9-azatricyclo[9.4.0.0³,⁸]pentadeca-1(11),3,5,7,9,12,14-heptaene | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | loxapine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CN1CCN(CC1)C1=NC2=CC=CC=C2OC2=C1C=C(Cl)C=C2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C18H18ClN3O/c1-21-8-10-22(11-9-21)18-14-12-13(19)6-7-16(14)23-17-5-3-2-4-15(17)20-18/h2-7,12H,8-11H2,1H3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=XJGVXQDUIWGIRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as dibenzoxazepines. Dibenzoxazepines are compounds containing a dibenzoxazepine moiety, which consists of two benzene connected by an oxazepine ring. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Benzoxazepines | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Dibenzoxazepines | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Dibenzoxazepines | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Oral, Intramuscular. Systemic bioavailability of the parent drug was only about one third that after an equivalent intramuscular dose (25 mg base) in male volunteers. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Loxapine is a dopamine antagonist, and also a serotonin 5-HT2 blocker. The exact mode of action of Loxapine has not been established, however changes in the level of excitability of subcortical inhibitory areas have been observed in several animal species in association with such manifestations of tranquilization as calming effects and suppression of aggressive behavior. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Hepatic Route of Elimination: Metabolites are excreted in the urine in the form of conjugates and in the feces unconjugated. Half Life: Oral-4 hours | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50=65 mg/kg (Orally in mice) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | For the management of the manifestations of psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | LD50=65 mg/kg (Orally in mice) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | The treatment of overdosage is essentially symptomatic and supportive. Early gastric lavage and extended dialysis might be expected to be beneficial. Centrally-acting emetics may have little effect because of the antiemetic action of loxapine. In addition, emesis should be avoided because of the possibility of aspiration of vomitus. Avoid analeptics, such as pentylenetetrazol, which may cause convulsions. Severe hypotension might be expected to respond to the administration of levarterenol or phenylephrine. Epinephrine should not be used since its use in a patient with partial adrenergic blockade may further lower the blood pressure. Severe extrapyramidal reactions should be treated with anticholinergic antiparkinson agents or diphenhydramine hydrochloride, and anticonvulsant therapy should be initiated as indicated. Additional measures include oxygen and intravenous fluids. (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB00408 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB14552 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 3964 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL831 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 3827 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C07104 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 50841 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Loxapine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Loxapine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | U.S. Patents 3,412,193; 3,546,226. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D2779.pdf | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Potassium channel regulator activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14416
- Molecular Weight:
- 50618.91 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.021 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
| IC50 | 0.054 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Lee T, Tang SW: Loxapine and clozapine decrease serotonin (S2) but do not elevate dopamine (D2) receptor numbers in the rat brain. Psychiatry Res. 1984 Aug;12(4):277-85. [6239298 ]
- Hjerde E, Dahl SG, Sylte I: Atypical and typical antipsychotic drug interactions with the dopamine D2 receptor. Eur J Med Chem. 2005 Feb;40(2):185-94. [15694653 ]
- Kalkman HO, Neumann V, Nozulak J, Tricklebank MD: Cataleptogenic effect of subtype selective 5-HT receptor antagonists in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998 Feb 19;343(2-3):201-7. [9570468 ]
- Froimowitz M, Cody V: Biologically active conformers of phenothiazines and thioxanthenes. Further evidence for a ligand model of dopamine D2 receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1993 Jul 23;36(15):2219-27. [8101879 ]
- Froimowitz M, Cody V: The incorporation of butyrophenones and related compounds into a pharmacophore for dopamine D2 antagonists. Drug Des Discov. 1997 Aug;15(2):63-81. [9342550 ]
- Liao Y, Venhuis BJ, Rodenhuis N, Timmerman W, Wikstrom H, Meier E, Bartoszyk GD, Bottcher H, Seyfried CA, Sundell S: New (sulfonyloxy)piperazinyldibenzazepines as potential atypical antipsychotics: chemistry and pharmacological evaluation. J Med Chem. 1999 Jun 17;42(12):2235-44. [10377229 ]
- Phillips ST, de Paulis T, Neergaard JR, Baron BM, Siegel BW, Seeman P, Van Tol HH, Guan HC, Smith HE: Binding of 5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene and dibenz[b,f]oxepin analogues of clozapine to dopamine and serotonin receptors. J Med Chem. 1995 Feb 17;38(4):708-14. [7861418 ]
- Phillips ST, de Paulis T, Baron BM, Siegel BW, Seeman P, Van Tol HH, Guan HC, Smith HE: Binding of 5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepine and chiral 5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene analogues of clozapine to dopamine and serotonin receptors. J Med Chem. 1994 Aug 19;37(17):2686-96. [8064797 ]
- General Function:
- Sh3 domain binding
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor responsible for neuronal signaling in the mesolimbic system of the brain, an area of the brain that regulates emotion and complex behavior. Its activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Modulates the circadian rhythm of contrast sensitivity by regulating the rhythmic expression of NPAS2 in the retinal ganglion cells (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- DRD4
- Uniprot ID:
- P21917
- Molecular Weight:
- 48359.86 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0049 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
| Inhibitory | 0.009 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
| IC50 | 0.014 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Liao Y, Venhuis BJ, Rodenhuis N, Timmerman W, Wikstrom H, Meier E, Bartoszyk GD, Bottcher H, Seyfried CA, Sundell S: New (sulfonyloxy)piperazinyldibenzazepines as potential atypical antipsychotics: chemistry and pharmacological evaluation. J Med Chem. 1999 Jun 17;42(12):2235-44. [10377229 ]
- Phillips ST, de Paulis T, Neergaard JR, Baron BM, Siegel BW, Seeman P, Van Tol HH, Guan HC, Smith HE: Binding of 5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene and dibenz[b,f]oxepin analogues of clozapine to dopamine and serotonin receptors. J Med Chem. 1995 Feb 17;38(4):708-14. [7861418 ]
- Phillips ST, de Paulis T, Baron BM, Siegel BW, Seeman P, Van Tol HH, Guan HC, Smith HE: Binding of 5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepine and chiral 5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene analogues of clozapine to dopamine and serotonin receptors. J Med Chem. 1994 Aug 19;37(17):2686-96. [8064797 ]
- Liegeois JF, Deville M, Dilly S, Lamy C, Mangin F, Resimont M, Tarazi FI: New pyridobenzoxazepine derivatives derived from 5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-8-chloro-pyrido[2,3-b][1,5]benzoxazepine (JL13): chemical synthesis and pharmacological evaluation. J Med Chem. 2012 Feb 23;55(4):1572-82. doi: 10.1021/jm2013419. Epub 2012 Feb 13. [22268448 ]
- General Function:
- Virus receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including mescaline, psilocybin, 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates phospholipase C and a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Affects neural activity, perception, cognition and mood. Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including responses to anxiogenic situations and psychoactive substances. Plays a role in intestinal smooth muscle contraction, and may play a role in arterial vasoconstriction.(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human JC polyomavirus/JCPyV.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P28223
- Molecular Weight:
- 52602.58 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.002 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
| Inhibitory | 0.00242 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Li Z, Ichikawa J, Meltzer HY: A comparison of the effects of loxapine with ziprasidone and thioridazine on the release of dopamine and acetylcholine in the prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003 May;167(3):315-23. Epub 2003 Mar 28. [12664192 ]
- Seeman P, Tallerico T: Antipsychotic drugs which elicit little or no parkinsonism bind more loosely than dopamine to brain D2 receptors, yet occupy high levels of these receptors. Mol Psychiatry. 1998 Mar;3(2):123-34. [9577836 ]
- Liegeois JF, Deville M, Dilly S, Lamy C, Mangin F, Resimont M, Tarazi FI: New pyridobenzoxazepine derivatives derived from 5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-8-chloro-pyrido[2,3-b][1,5]benzoxazepine (JL13): chemical synthesis and pharmacological evaluation. J Med Chem. 2012 Feb 23;55(4):1572-82. doi: 10.1021/jm2013419. Epub 2012 Feb 13. [22268448 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase. It has a high affinity for tricyclic psychotropic drugs (By similarity). Controls pyramidal neurons migration during corticogenesis, through the regulation of CDK5 activity (By similarity). Is an activator of TOR signaling (PubMed:23027611).
- Gene Name:
- HTR6
- Uniprot ID:
- P50406
- Molecular Weight:
- 46953.625 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.015 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
| Inhibitory | 0.027 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Glennon RA: Higher-end serotonin receptors: 5-HT(5), 5-HT(6), and 5-HT(7). J Med Chem. 2003 Jul 3;46(14):2795-812. [12825922 ]
- Kohen R, Metcalf MA, Khan N, Druck T, Huebner K, Lachowicz JE, Meltzer HY, Sibley DR, Roth BL, Hamblin MW: Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization of a human 5-HT6 serotonin receptor. J Neurochem. 1996 Jan;66(1):47-56. [8522988 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled acetylcholine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is adenylate cyclase inhibition. Signaling promotes phospholipase C activity, leading to the release of inositol trisphosphate (IP3); this then triggers calcium ion release into the cytosol.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM2
- Uniprot ID:
- P08172
- Molecular Weight:
- 51714.605 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.3 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
| Inhibitory | 0.45 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E: Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):576-80. [1346637 ]
- Richelson E, Nelson A: Antagonism by neuroleptics of neurotransmitter receptors of normal human brain in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 17;103(3-4):197-204. [6149136 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including ergot alkaloid derivatives, 1-2,5,-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and down-stream signaling cascades and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Regulates neuronal activity via the activation of short transient receptor potential calcium channels in the brain, and thereby modulates the activation of pro-opiomelacortin neurons and the release of CRH that then regulates the release of corticosterone. Plays a role in the regulation of appetite and eating behavior, responses to anxiogenic stimuli and stress. Plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P28335
- Molecular Weight:
- 51820.705 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.017 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Herrick-Davis K, Grinde E, Teitler M: Inverse agonist activity of atypical antipsychotic drugs at human 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Oct;295(1):226-32. [10991983 ]
- General Function:
- Thioesterase binding
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is oxymetazoline > clonidine > epinephrine > norepinephrine > phenylephrine > dopamine > p-synephrine > p-tyramine > serotonin = p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > phentolamine = mianserine > chlorpromazine = spiperone = prazosin > propanolol > alprenolol = pindolol.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08913
- Molecular Weight:
- 48956.275 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 2.4 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Richelson E, Nelson A: Antagonism by neuroleptics of neurotransmitter receptors of normal human brain in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 17;103(3-4):197-204. [6149136 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21728
- Molecular Weight:
- 49292.765 Da
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Promotes cell proliferation.
- Gene Name:
- DRD3
- Uniprot ID:
- P35462
- Molecular Weight:
- 44224.335 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 0.022 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Liao Y, Venhuis BJ, Rodenhuis N, Timmerman W, Wikstrom H, Meier E, Bartoszyk GD, Bottcher H, Seyfried CA, Sundell S: New (sulfonyloxy)piperazinyldibenzazepines as potential atypical antipsychotics: chemistry and pharmacological evaluation. J Med Chem. 1999 Jun 17;42(12):2235-44. [10377229 ]
- General Function:
- Histamine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- In peripheral tissues, the H1 subclass of histamine receptors mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, and catecholamine release from adrenal medulla, as well as mediating neurotransmission in the central nervous system.
- Gene Name:
- HRH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P35367
- Molecular Weight:
- 55783.61 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0049 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Richelson E, Nelson A: Antagonism by neuroleptics of neurotransmitter receptors of normal human brain in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 17;103(3-4):197-204. [6149136 ]
- General Function:
- Phosphatidylinositol phospholipase c activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11229
- Molecular Weight:
- 51420.375 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0639 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E: Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):576-80. [1346637 ]
- General Function:
- Receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM3
- Uniprot ID:
- P20309
- Molecular Weight:
- 66127.445 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.39 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E: Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):576-80. [1346637 ]
- General Function:
- Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is inhibition of adenylate cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM4
- Uniprot ID:
- P08173
- Molecular Weight:
- 53048.65 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.3 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 22871 |
References
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E: Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):576-80. [1346637 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity and activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that regulates the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Plays a role in the regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release and in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism. Plays a role in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, mood and behavior. Plays a role in the response to anxiogenic stimuli.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08908
- Molecular Weight:
- 46106.335 Da
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for ergot alkaloid derivatives, various anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs and other psychoactive substances, such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. Arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Regulates the release of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine and acetylcholine in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, nociceptive processing, pain perception, mood and behavior. Besides, plays a role in vasoconstriction of cerebral arteries.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P28222
- Molecular Weight:
- 43567.535 Da
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for ergot alkaloid derivatives, various anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs and other psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. Regulates the release of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity. May also play a role in regulating the release of other neurotransmitters. May play a role in vasoconstriction.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1D
- Uniprot ID:
- P28221
- Molecular Weight:
- 41906.38 Da
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various alkaloids and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1E
- Uniprot ID:
- P28566
- Molecular Weight:
- 41681.57 Da
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated potassium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. This receptor is a ligand-gated ion channel, which when activated causes fast, depolarizing responses in neurons. It is a cation-specific, but otherwise relatively nonselective, ion channel.
- Gene Name:
- HTR3A
- Uniprot ID:
- P46098
- Molecular Weight:
- 55279.835 Da
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins.
- Gene Name:
- HTR5A
- Uniprot ID:
- P47898
- Molecular Weight:
- 40254.69 Da
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- HTR7
- Uniprot ID:
- P34969
- Molecular Weight:
- 53554.43 Da
- General Function:
- Protein heterodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- This alpha-adrenergic receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Its effect is mediated by G(q) and G(11) proteins. Nuclear ADRA1A-ADRA1B heterooligomers regulate phenylephrine(PE)-stimulated ERK signaling in cardiac myocytes.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P35348
- Molecular Weight:
- 51486.005 Da
- General Function:
- Protein heterodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- This alpha-adrenergic receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Its effect is mediated by G(q) and G(11) proteins. Nuclear ADRA1A-ADRA1B heterooligomers regulate phenylephrine (PE)-stimulated ERK signaling in cardiac myocytes.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P35368
- Molecular Weight:
- 56835.375 Da
- General Function:
- Epinephrine binding
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is clonidine > norepinephrine > epinephrine = oxymetazoline > dopamine > p-tyramine = phenylephrine > serotonin > p-synephrine / p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > chlorpromazine > phentolamine > mianserine > spiperone > prazosin > alprenolol > propanolol > pindolol.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2B
- Uniprot ID:
- P18089
- Molecular Weight:
- 49565.8 Da
- General Function:
- Protein homodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P18825
- Molecular Weight:
- 49521.585 Da
- General Function:
- Receptor signaling protein activity
- Specific Function:
- Beta-adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced activation of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. This receptor binds epinephrine and norepinephrine with approximately equal affinity. Mediates Ras activation through G(s)-alpha- and cAMP-mediated signaling.
- Gene Name:
- ADRB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08588
- Molecular Weight:
- 51322.1 Da
26. D(1) dopamine receptor (Protein Group)
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD5
- Uniprot ID:
- P21918
- Molecular Weight:
- 52950.5 Da
- General Function:
- Histamine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- The H2 subclass of histamine receptors mediates gastric acid secretion. Also appears to regulate gastrointestinal motility and intestinal secretion. Possible role in regulating cell growth and differentiation. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase and, through a separate G protein-dependent mechanism, the phosphoinositide/protein kinase (PKC) signaling pathway (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- HRH2
- Uniprot ID:
- P25021
- Molecular Weight:
- 40097.65 Da
- General Function:
- Histamine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- The H4 subclass of histamine receptors could mediate the histamine signals in peripheral tissues. Displays a significant level of constitutive activity (spontaneous activity in the absence of agonist).
- Gene Name:
- HRH4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9H3N8
- Molecular Weight:
- 44495.375 Da
- General Function:
- Phosphatidylinositol phospholipase c activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM5
- Uniprot ID:
- P08912
- Molecular Weight:
- 60073.205 Da
- General Function:
- Monoamine transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Amine transporter. Terminates the action of dopamine by its high affinity sodium-dependent reuptake into presynaptic terminals.
- Gene Name:
- SLC6A3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q01959
- Molecular Weight:
- 68494.255 Da
- General Function:
- Norepinephrine:sodium symporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Amine transporter. Terminates the action of noradrenaline by its high affinity sodium-dependent reuptake into presynaptic terminals.
- Gene Name:
- SLC6A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P23975
- Molecular Weight:
- 69331.42 Da
- General Function:
- Serotonin:sodium symporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Serotonin transporter whose primary function in the central nervous system involves the regulation of serotonergic signaling via transport of serotonin molecules from the synaptic cleft back into the pre-synaptic terminal for re-utilization. Plays a key role in mediating regulation of the availability of serotonin to other receptors of serotonergic systems. Terminates the action of serotonin and recycles it in a sodium-dependent manner.
- Gene Name:
- SLC6A4
- Uniprot ID:
- P31645
- Molecular Weight:
- 70324.165 Da