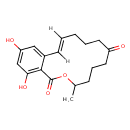
(S,E)-Zearalenone (T3D3665)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-12-22 23:09:04 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:19 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D3665 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | (S,E)-Zearalenone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | cis-Zearalenone is a metabolite of Fusarium species. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C18H22O5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 318.364 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 318.147 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 17924-92-4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 14,16-dihydroxy-3-methyl-3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10-octahydro-1H-2-benzoxacyclotetradecine-1,7-dione | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | zearalenone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H]\C1=C([H])/C2=CC(O)=CC(O)=C2C(=O)OC(C)CCCC(=O)CCC1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C18H22O5/c1-12-6-5-9-14(19)8-4-2-3-7-13-10-15(20)11-16(21)17(13)18(22)23-12/h3,7,10-12,20-21H,2,4-6,8-9H2,1H3/b7-3+ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=MBMQEIFVQACCCH-XVNBXDOJNA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as zearalenones. These are macrolides which contains a fourteen-member lactone fused to 1,3-dihydroxybenzene. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Phenylpropanoids and polyketides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Macrolides and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Zearalenones | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Zearalenones | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White crystalline solid. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Oral, dermal, inhalation, and parenteral (contaminated drugs). (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Zearalenone's genotoxicity results from it's ability to cause DNA fragmentation, chromosome aberrations, and DNA adduct formation. It exerts cytotoxic effects by enhancing lipid peroxidation, increasing oxidative stress, and inducing apoptosis. Zearalenone also has significant estrogenic activity, causing severe reproductive problems in animals. In humans, Zearalenone has been shown to cause an earlier onset of puberty in children, endometrial adenocarcinomas, hyperplasia and breast cancer in women. Mycotoxins are often able to enter the liver and kidney by human organic anion transporters (hOATs) and human organic cation transporters (hOCTs). They can also inhibit uptake of anions and cations by these transporters, interefering with the secretion of endogenous metabolites, drugs, and xenobiotics including themselves. This results in increased cellular accumulation of toxic compounds causing nephro- and hepatotoxicity. (1, 2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Zearalenone is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. In humans, most of the zearalenone absorbed is not metabolized. The main metabolites include alpha- and beta-zeralenol, and the glucuronide conjugates of both the parent compound and its metabolites. Zearalenone and its metabolites are excreted mainly in the bile. (4, 9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: >2000 mg/kg (Oral, Mouse) (9) LD50: >500 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal, Mouse) (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 3, not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. (8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Zearalenone (ZEA), also known as RAL and F-2 mycotoxin, is a potent estrogenic metabolite produced by some Giberella species. Several Fusarium species also produce zearalenone as their primary toxin. It can be found worldwide in a number of cereal crops, such as maize, barley, oats, wheat, rice, and sorghum, and also in bread. (10) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Zearalenone is a reproductive toxin and has been shown to cause infertility, abortion or other breeding problems in livestock. In humans it can cause earlier onset of puberty in children, endometrial adenocarcinomas, hyperplasia, and breast cancer in women. Zearalenone is also immunotoxic, genotoxic, and can cause kidney and liver damage. (10, 1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB31752 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 5375083 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 4524664 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C09981 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Zearalenone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D3665.pdf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.00 uM | ACEA_T47D_80hr_Positive | ACEA Biosciences |
| AC50 | 0.03 uM | ATG_ERa_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.01 uM | ATG_ERE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.00 uM | NVS_NR_hER | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 0.79 uM | OT_ER_ERaERa_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 1.03 uM | OT_ER_ERaERa_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.21 uM | OT_ERa_EREGFP_0120 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.28 uM | OT_ERa_EREGFP_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.13 uM | Tox21_ERa_BLA_Agonist_ratio | Tox21/NCGC |
| AC50 | 8.23 uM | Tox21_ERa_BLA_Antagonist_ratio | Tox21/NCGC |
| AC50 | 0.00 uM | Tox21_ERa_LUC_BG1_Agonist | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Fitzpatrick DW, Picken CA, Murphy LC, Buhr MM: Measurement of the relative binding affinity of zearalenone, alpha-zearalenol and beta-zearalenol for uterine and oviduct estrogen receptors in swine, rats and chickens: an indicator of estrogenic potencies. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1989;94(2):691-4. [2576797 ]
- Takemura H, Shim JY, Sayama K, Tsubura A, Zhu BT, Shimoi K: Characterization of the estrogenic activities of zearalenone and zeranol in vivo and in vitro. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Feb;103(2):170-7. Epub 2006 Nov 9. [17097287 ]
- Wober J, Weisswange I, Vollmer G: Stimulation of alkaline phosphatase activity in Ishikawa cells induced by various phytoestrogens and synthetic estrogens. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002 Dec;83(1-5):227-33. [12650720 ]
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. Binds estrogens with an affinity similar to that of ESR1, and activates expression of reporter genes containing estrogen response elements (ERE) in an estrogen-dependent manner (PubMed:20074560). Isoform beta-cx lacks ligand binding ability and has no or only very low ere binding activity resulting in the loss of ligand-dependent transactivation ability. DNA-binding by ESR1 and ESR2 is rapidly lost at 37 degrees Celsius in the absence of ligand while in the presence of 17 beta-estradiol and 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen loss in DNA-binding at elevated temperature is more gradual.
- Gene Name:
- ESR2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q92731
- Molecular Weight:
- 59215.765 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.18 uM | OT_ER_ERaERb_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.52 uM | OT_ER_ERaERb_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.23 uM | OT_ER_ERbERb_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.10 uM | OT_ER_ERbERb_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
References
- Takemura H, Shim JY, Sayama K, Tsubura A, Zhu BT, Shimoi K: Characterization of the estrogenic activities of zearalenone and zeranol in vivo and in vitro. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Feb;103(2):170-7. Epub 2006 Nov 9. [17097287 ]
- Mueller SO, Simon S, Chae K, Metzler M, Korach KS: Phytoestrogens and their human metabolites show distinct agonistic and antagonistic properties on estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and ERbeta in human cells. Toxicol Sci. 2004 Jul;80(1):14-25. Epub 2004 Apr 14. [15084758 ]
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled estrogen receptor that binds to 17-beta-estradiol (E2) with high affinity, leading to rapid and transient activation of numerous intracellular signaling pathways. Stimulates cAMP production, calcium mobilization and tyrosine kinase Src inducing the release of heparin-bound epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) and subsequent transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), activating downstream signaling pathways such as PI3K/Akt and ERK/MAPK. Mediates pleiotropic functions among others in the cardiovascular, endocrine, reproductive, immune and central nervous systems. Has a role in cardioprotection by reducing cardiac hypertrophy and perivascular fibrosis in a RAMP3-dependent manner. Regulates arterial blood pressure by stimulating vasodilation and reducing vascular smooth muscle and microvascular endothelial cell proliferation. Plays a role in blood glucose homeostasis contributing to the insulin secretion response by pancreatic beta cells. Triggers mitochondrial apoptosis during pachytene spermatocyte differentiation. Stimulates uterine epithelial cell proliferation. Enhances uterine contractility in response to oxytocin. Contributes to thymic atrophy by inducing apoptosis. Attenuates TNF-mediated endothelial expression of leukocyte adhesion molecules. Promotes neuritogenesis in developing hippocampal neurons. Plays a role in acute neuroprotection against NMDA-induced excitotoxic neuronal death. Increases firing activity and intracellular calcium oscillations in luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) neurons. Inhibits early osteoblast proliferation at growth plate during skeletal development. Inhibits mature adipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation. Involved in the recruitment of beta-arrestin 2 ARRB2 at the plasma membrane in epithelial cells. Functions also as a receptor for aldosterone mediating rapid regulation of vascular contractibility through the PI3K/ERK signaling pathway. Involved in cancer progression regulation. Stimulates cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) proliferation by a rapid genomic response through the EGFR/ERK transduction pathway. Associated with EGFR, may act as a transcription factor activating growth regulatory genes (c-fos, cyclin D1). Promotes integrin alpha-5/beta-1 and fibronectin (FN) matrix assembly in breast cancer cells.
- Gene Name:
- GPER1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99527
- Molecular Weight:
- 42247.12 Da
References
- Thomas P, Dong J: Binding and activation of the seven-transmembrane estrogen receptor GPR30 by environmental estrogens: a potential novel mechanism of endocrine disruption. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 Dec;102(1-5):175-9. Epub 2006 Nov 7. [17088055 ]
- General Function:
- Secondary active organic cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Translocates a broad array of organic cations with various structures and molecular weights including the model compounds 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), tetraethylammonium (TEA), N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), 4-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-N-methylpyridinium (ASP), the endogenous compounds choline, guanidine, histamine, epinephrine, adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine, and the drugs quinine, and metformin. The transport of organic cations is inhibited by a broad array of compounds like tetramethylammonium (TMA), cocaine, lidocaine, NMDA receptor antagonists, atropine, prazosin, cimetidine, TEA and NMN, guanidine, cimetidine, choline, procainamide, quinine, tetrabutylammonium, and tetrapentylammonium. Translocates organic cations in an electrogenic and pH-independent manner. Translocates organic cations across the plasma membrane in both directions. Transports the polyamines spermine and spermidine. Transports pramipexole across the basolateral membrane of the proximal tubular epithelial cells. The choline transport is activated by MMTS. Regulated by various intracellular signaling pathways including inhibition by protein kinase A activation, and endogenously activation by the calmodulin complex, the calmodulin-dependent kinase II and LCK tyrosine kinase.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A1
- Uniprot ID:
- O15245
- Molecular Weight:
- 61153.345 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates saturable uptake of estrone sulfate, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and related compounds.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A11
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NSA0
- Molecular Weight:
- 59970.945 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Quaternary ammonium group transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates tubular uptake of organic compounds from circulation. Mediates the influx of agmatine, dopamine, noradrenaline (norepinephrine), serotonin, choline, famotidine, ranitidine, histamin, creatinine, amantadine, memantine, acriflavine, 4-[4-(dimethylamino)-styryl]-N-methylpyridinium ASP, amiloride, metformin, N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), tetraethylammonium (TEA), 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), cimetidine, cisplatin and oxaliplatin. Cisplatin may develop a nephrotoxic action. Transport of creatinine is inhibited by fluoroquinolones such as DX-619 and LVFX. This transporter is a major determinant of the anticancer activity of oxaliplatin and may contribute to antitumor specificity.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A2
- Uniprot ID:
- O15244
- Molecular Weight:
- 62579.99 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in the renal elimination of endogenous and exogenous organic anions. Functions as organic anion exchanger when the uptake of one molecule of organic anion is coupled with an efflux of one molecule of endogenous dicarboxylic acid (glutarate, ketoglutarate, etc). Mediates the sodium-independent uptake of 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid (DMPS) (By similarity). Mediates the sodium-independent uptake of p-aminohippurate (PAH), ochratoxin (OTA), acyclovir (ACV), 3'-azido-3-'deoxythymidine (AZT), cimetidine (CMD), 2,4-dichloro-phenoxyacetate (2,4-D), hippurate (HA), indoleacetate (IA), indoxyl sulfate (IS) and 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropionate (CMPF), cidofovir, adefovir, 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl) guanine (PMEG), 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl) diaminopurine (PMEDAP) and edaravone sulfate. PAH uptake is inhibited by p-chloromercuribenzenesulphonate (PCMBS), diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC), sulindac, diclofenac, carprofen, glutarate and okadaic acid (By similarity). PAH uptake is inhibited by benzothiazolylcysteine (BTC), S-chlorotrifluoroethylcysteine (CTFC), cysteine S-conjugates S-dichlorovinylcysteine (DCVC), furosemide, steviol, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), calcium ionophore A23187, benzylpenicillin, furosemide, indomethacin, bumetamide, losartan, probenecid, phenol red, urate, and alpha-ketoglutarate.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q4U2R8
- Molecular Weight:
- 61815.78 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates sodium-independent multispecific organic anion transport. Transport of prostaglandin E2, prostaglandin F2, tetracycline, bumetanide, estrone sulfate, glutarate, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, allopurinol, 5-fluorouracil, paclitaxel, L-ascorbic acid, salicylate, ethotrexate, and alpha-ketoglutarate.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A7
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9Y694
- Molecular Weight:
- 60025.025 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Plays an important role in the excretion/detoxification of endogenous and exogenous organic anions, especially from the brain and kidney. Involved in the transport basolateral of steviol, fexofenadine. Transports benzylpenicillin (PCG), estrone-3-sulfate (E1S), cimetidine (CMD), 2,4-dichloro-phenoxyacetate (2,4-D), p-amino-hippurate (PAH), acyclovir (ACV) and ochratoxin (OTA).
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A8
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8TCC7
- Molecular Weight:
- 59855.585 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Oxygen binding
- Specific Function:
- Catalyzes the formation of aromatic C18 estrogens from C19 androgens.
- Gene Name:
- CYP19A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11511
- Molecular Weight:
- 57882.48 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.08 uM | Tox21_Aromatase_Inhibition | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes.
- Gene Name:
- NR1I2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75469
- Molecular Weight:
- 49761.245 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.47 uM | ATG_PXR_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 1.90 uM | ATG_PXRE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.63 uM | NVS_NR_hPXR | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. Transcription factor that mediates the action of vitamin D3 by controlling the expression of hormone sensitive genes. Recruited to promoters via its interaction with BAZ1B/WSTF which mediates the interaction with acetylated histones, an essential step for VDR-promoter association. Plays a central role in calcium homeostasis.
- Gene Name:
- VDR
- Uniprot ID:
- P11473
- Molecular Weight:
- 48288.64 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 5.59 uM | ATG_VDRE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Steroid hormone receptors are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Transcription factor activity is modulated by bound coactivator and corepressor proteins. Transcription activation is down-regulated by NR0B2. Activated, but not phosphorylated, by HIPK3 and ZIPK/DAPK3.
- Gene Name:
- AR
- Uniprot ID:
- P10275
- Molecular Weight:
- 98987.9 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 6.72 uM | NVS_NR_hAR | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Once activated by a ligand, the nuclear receptor binds to DNA specific PPAR response elements (PPRE) and modulates the transcription of its target genes, such as acyl-CoA oxidase. It therefore controls the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Key regulator of adipocyte differentiation and glucose homeostasis. ARF6 acts as a key regulator of the tissue-specific adipocyte P2 (aP2) enhancer. Acts as a critical regulator of gut homeostasis by suppressing NF-kappa-B-mediated proinflammatory responses. Plays a role in the regulation of cardiovascular circadian rhythms by regulating the transcription of ARNTL/BMAL1 in the blood vessels (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- PPARG
- Uniprot ID:
- P37231
- Molecular Weight:
- 57619.58 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 9.06 uM | ATG_PPARg_TRANS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]