| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-30 17:59:08 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:07 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3532 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Salvinorin A |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Salvinorin A is the main active psychotropic molecule in Salvia divinorum, a Mexican plant which has a long history of use as an entheogen by indigenous Mazatec shamans. Salvinorin A is a hallucinogenic compound with dissociative effects (10). |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Ester
- Ether
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
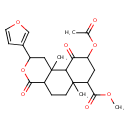
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Diviner's sage | | Divinorin a | | Herbal ecstasy | | Mexican mint | | Salvinorin | | Salvinorin a | | Ska maria pastora |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C23H28O8 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 432.464 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 432.178 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 83729-01-5 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | methyl 9-(acetyloxy)-2-(furan-3-yl)-6a,10b-dimethyl-4,10-dioxo-dodecahydro-1H-naphtho[2,1-c]pyran-7-carboxylate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | methyl 9-(acetyloxy)-2-(furan-3-yl)-6a,10b-dimethyl-4,10-dioxo-octahydro-1H-naphtho[2,1-c]pyran-7-carboxylate |
|---|
| SMILES | COC(=O)C1CC(OC(C)=O)C(=O)C2C1(C)CCC1C(=O)OC(CC21C)C1=COC=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C23H28O8/c1-12(24)30-16-9-15(20(26)28-4)22(2)7-5-14-21(27)31-17(13-6-8-29-11-13)10-23(14,3)19(22)18(16)25/h6,8,11,14-17,19H,5,7,9-10H2,1-4H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=OBSYBRPAKCASQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as diterpene lactones. These are diterpenoids containing a lactone moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Terpene lactones |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Diterpene lactones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Diterpene lactone
- Diterpenoid
- Clerodane diterpenoid
- Naphthopyran
- Naphthalene
- Tricarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Delta valerolactone
- Delta_valerolactone
- Alpha-acyloxy ketone
- Pyran
- Oxane
- Methyl ester
- Furan
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Ketone
- Lactone
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | Colorless crystals from methanol (2). |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 238-244°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-006x-5079300000-0c3d81b169f1ec02eb08 | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-001i-1008900000-3dde4855bc69f27483e4 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0gi3-1019500000-0d06ceb5fd22972dfc1e | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0gxw-3249100000-797004a599225d2018a4 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-001r-3009600000-a9c68bc515eddd483f7d | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a5i-3009200000-0bf80f4121126284c9d4 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9006000000-f6147bd53d5e352b972c | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00di-0009200000-3c86e6f8f5d793dd7a0b | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-001i-0019100000-511b0cc4a7bbe7ac17a2 | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0002-9057100000-1307ddb5b9baf63a568b | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000200000-4490b6cd9718932fc15b | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9002000000-18739f0784b8f7ec39da | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a6v-9036300000-46b86aa451b8356c46c8 | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Ingestion (11) ; dermal (11) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Salvinorin A, the active component of the hallucinogenic sage Salvia divinorum, is an apparently selective and highly potent kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) agonist. Salvinorin A is unique among ligands for peptidergic G protein-coupled receptors in being nonnitrogenous and lipid-like in character (3). |
|---|
| Metabolism | Salvinorin A’s chemical structure suggests that it may be a substrate of CYP450 (oxidative metabolism), UGT (hydrolysis) or carboxylesterases (ChEs) (hydrolysis). In addition, as observed for CYP1A1, CPY2C18 and CYP2E1, Salvinorin A metabolism via UGTB27 appears to be saturable at higher concentrations. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity (not listed by IARC). (12) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Traditional medicine used by the Mazatec people of Oaxaca, Mexico (2). |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Psychedelic-like changes in visual perception, mood, and body sensations (4). |
|---|
| Symptoms | Hallucinations or delusional episodes that mimic psychosis. ; emotional swings; feelings of detachment; and importantly, a highly modified perception of external reality and the self, which leads to a decreased ability to interact with one's surroundings (4). |
|---|
| Treatment | Treatment for salvinorin A overdose would be similar to the treatments for hallucinogen intoxication. (5) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 128563 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Salvinorin A |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Salvinorin |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D3532.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Teksin ZS, Lee IJ, Nemieboka NN, Othman AA, Upreti VV, Hassan HE, Syed SS, Prisinzano TE, Eddington ND: Evaluation of the transport, in vitro metabolism and pharmacokinetics of Salvinorin A, a potent hallucinogen. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009 Jun;72(2):471-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2009.01.002. [19462483 ]
- McAlister ED, Van Vugt DA: Effect of leptin administration versus re-feeding on hypothalamic neuropeptide gene expression in fasted male rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2004 Dec;82(12):1128-34. [15644956 ]
- Muhlhausler BS, Adam CL, Marrocco EM, Findlay PA, Roberts CT, McFarlane JR, Kauter KG, McMillen IC: Impact of glucose infusion on the structural and functional characteristics of adipose tissue and on hypothalamic gene expression for appetite regulatory neuropeptides in the sheep fetus during late gestation. J Physiol. 2005 May 15;565(Pt 1):185-95. Epub 2005 Jan 20. [15661821 ]
- Loos RJ, Rankinen T, Tremblay A, Perusse L, Chagnon Y, Bouchard C: Melanocortin-4 receptor gene and physical activity in the Quebec Family Study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005 Apr;29(4):420-8. [15597110 ]
- Scruggs P, Lai CC, Scruggs JE, Dun NJ: Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide potentiates spinal glutamatergic sympathoexcitation in anesthetized rats. Regul Pept. 2005 Apr 15;127(1-3):79-85. [15680473 ]
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) (2007). Infofacts: Salvia.
- O'Neil MJ (ed) (2006). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th ed. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc.
- Vortherms TA et al; J Biol Chem 282 (5): 3146-56 (2007).
- Biller J (2007). The Interface of Neurology & Internal Medicine. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health, Lippincott/Williams and Wilkins.
- Wikipedia. Salvinorin. Last Updated 8 August 2009. [Link]
- Wikipedia. Phytotoxin. Last Updated 7 August 2009. [Link]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (2014). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|