| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:27:05 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:51 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2815 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Dextromethorphan |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Dextromethorphan is an antitussive drug that is found in many over-the-counter cold and cough preparations, usually in the form of dextromethorphan hydrobromide. Dextromethorphan is a salt of the methyl ether dextrorotatory isomer of levorphanol, a narcotic analgesic. Dextromethorphan occurs as white crystals, is sparingly soluble in water, and freely soluble in alcohol. The drug is dextrorotatory in water (at 20 degrees Celsius, Sodium D-line) with a specific rotation of +27.6 degrees. Following oral administration, dextromethorphan is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, where it enters the bloodstream and crosses the blood-brain barrier. Dextromethorphan shows high affinity binding to several regions of the brain, including the medullary cough center. The first-pass through the hepatic portal vein results in some of the drug being metabolized into an active metabolite of dextromethorphan, dextrorphan, the 3-hydroxy derivative of dextromethorphan. The therapeutic activity of dextromethorphan is believed to be caused by both the drug and this metabolite. Dextromethorphan is predominantly metabolized by the liver, by various hepatic enzymes. Through various pathways, the drug undergoes (O-demethylation (which produces dextrorphan), N-demethylation, and partial conjugation with glucuronic acid and sulfate ions. The inactive metabolite (+)-3-hydroxy-N-methylmorphinan is formed as a product of DXM metabolism by these pathways. One well known metabolic catalyst involved is a specific cytochrome P450 enzyme known as 2D6, or CYP2D6. A significant portion of the population has a functional deficiency in this enzyme (and are known as poor CYP2D6 metabolizers). As CYP2D6 is the primary metabolic pathway in the inactivation of dextromethorphan, the duration of action and effects of dextromethorphan are significantly increased in such poor metabolizers. Deaths and hospitalizations have been reported in recreational use by poor CYP2D6 metabolizers. -- Wikipedia. This compound is an NMDA receptor antagonist (receptors, N-methyl-D-aspartate) and acts as a non-competitive channel blocker. It is also used to study the involvement of glutamate receptors in neurotoxicity. [PubChem] It is also the d-isomer of the codeine analog of levorphanol. Dextromethorphan shows high affinity binding to several regions of the brain, including the medullary cough center. This compound is an NMDA receptor antagonist (receptors, N-methyl-D-aspartate) and acts as a non-competitive channel blocker. It is one of the widely used antitussives, and is also used to study the involvement of glutamate receptors in neurotoxicity. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Analgesic, Opioid
- Antitussive Agent
- Drug
- Ether
- Excitatory Amino Acid Antagonist
- Food Toxin
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
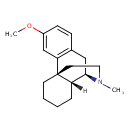
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Balminil DM | | Bayer Select Flu Relief | | Bayer Select Head & Chest Cold | | Bayer Select Night Time Cold | | Benylin DM | | Benylin dm | | Cerose-DM | | Chloraseptic DM | | Contac Day & Night Cold/Flu Day Caplets | | Contac Jr. Non-drowsy Formula | | Contac Nighttime Cold Medicine | | Contac Severe Cold Formula Maximum Strength | | Contac Severe Cold Formula Non-Drowsy | | Coricidin Syrup | | Cough-X | | D-Methorphan | | D-Methorphan Hydrobromide | | Delsym | | delta-Methorphan | | Demorphan | | Demorphan Hydrobromide | | Demorphine | | Destrometerfano | | Dextromethorfan | | Dextromethorphan Bromhydrate | | Dextromethorphan Bromide | | Dextromethorphan hydrobromide | | Dextromethorphan hydrobromide monohydrate | | Dextromethorphan hydrobromide OROS Tablets | | Dextrométhorphane | | Dextromethorphanum | | Dextrometorfano | | Dextrometorphan | | Dextromorphan | | Dexyromethorphan | | Dimacol | | Dimetapp DM | | DM | | DMHM | | Drixoral Cough | | Drixoral Cough & Congestion | | Drixoral Cough & Sore Throat | | DXM | | Endotussin-NN | | Endotussin-NN Pediatric | | Hold | | Koffex DM | | L-Methorphan | | Levomethorphan | | Methorate | | Naldecon-DX | | Ornex Severe Cold Formula | | Orthoxicol | | PediaCare 1 | | PediaCare Cough-Cold Formula | | Prestwick_686 | | Robitussin CF | | Robitussin Cold & Cough | | Robitussin Cough Calmers | | Robitussin DM | | Robitussin Maximum Strength Cough | | Robitussin pediatric cough | | Robitussin Pediatric Cough & Cold | | Robitussin Pediatric Night Relief | | Romilar | | Rondec dm | | Ru-Tuss Expectorant | | St. Joseph Cough Syrup | | Sudafed Cough Syrup | | Triaminic | | Trind-DM | | Tussar DM | | Tussi-Organidin | | Tussi-Organidin DM NR | | Tussi-Organidin DM-S NR | | Tylenol Cold and Flu Multi-Symptom | | Tylenol Cold and Flu No Drowsiness | | Tylenol Cold No Drowsiness | | Tylenol Cough + Decongestant Liquid | | Tylenol Cough Liquid | | Tylenol Flu No Drowsiness Gelcaps | | Vicks Formula 44 | | Viro-Med |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C18H25NO |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 271.397 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 271.194 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 125-71-3 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (1R,9R,10R)-4-methoxy-17-methyl-17-azatetracyclo[7.5.3.0^{1,10}.0^{2,7}]heptadeca-2(7),3,5-triene |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (1R,9R,10R)-4-methoxy-17-methyl-17-azatetracyclo[7.5.3.0^{1,10}.0^{2,7}]heptadeca-2(7),3,5-triene |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]12CC3=C(C=C(OC)C=C3)[C@]3(CCCC[C@@]13[H])CCN2C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C18H25NO/c1-19-10-9-18-8-4-3-5-15(18)17(19)11-13-6-7-14(20-2)12-16(13)18/h6-7,12,15,17H,3-5,8-11H2,1-2H3/t15-,17+,18+/s2 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=MKXZASYAUGDDCJ-HPAQEFICNA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as morphinans. These are polycyclic compounds with a four-ring skeleton with three condensed six-member rings forming a partially hydrogenated phenanthrene moiety, one of which is aromatic while the two others are alicyclic. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Alkaloids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Morphinans |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Morphinans |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Morphinan
- Phenanthrene
- Benzazocine
- Tetralin
- Anisole
- Alkyl aryl ether
- Aralkylamine
- Piperidine
- Benzenoid
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Tertiary amine
- Azacycle
- Ether
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Amine
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 122-124°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 74.7 mg/L | | LogP | 3.6 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0ab9-9640000000-22a67aaa9771bdc70ea1 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0ab9-9640000000-22a67aaa9771bdc70ea1 | 2018-05-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-054o-0190000000-5d924eb9e80a3ad52d7b | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 10V, N/A (Annotated) | splash10-0006-2931000000-7ed39f5c12687bd18073 | 2018-05-25 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 25V, N/A (Annotated) | splash10-001i-9450000000-484ef060149382ae3835 | 2018-05-25 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 40V, N/A (Annotated) | splash10-004i-0296000000-9cc5da1af6297bf41d6a | 2018-05-25 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00di-0090000000-25cdbb74a0783952c40e | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00di-0090000000-8062e3b60f2d8d6c78b9 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0btc-3290000000-e2bedc154835e1c44dbc | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00di-0090000000-cdc95ffda5c8ab176bc0 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-00di-0090000000-82ba173765c1d557ad82 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0udl-0190000000-f4f99127c0b1de038b01 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00di-0090000000-01488ff14969daea9a7c | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00di-0090000000-a31adf377a9c1f79d0fa | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0h2b-2790000000-0c7169ca6b6ad7325e80 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00di-0090000000-429ffca83bb47ee26787 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-00di-0090000000-429ffca83bb47ee26787 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0jba-0190000000-8b48abf42b5c1c70d082 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, CD3OD, experimental) | Not Available | 2018-05-25 | View Spectrum | | 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, CD3OD, experimental) | Not Available | 2018-05-25 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral, rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Dextromethorphan is an opioid-like drug that binds to and acts as antagonist to the NMDA glutamatergic receptor, it is an agonist to the opioid sigma 1 and sigma 2 receptors, it is also an alpha3/beta4 nicotinic receptor antagonist and targets the serotonin reuptake pump. Dextromethorphan is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, where it enters the bloodstream and crosses the blood-brain barrier. The first-pass through the hepatic portal vein results in some of the drug being metabolized into an active metabolite of dextromethorphan, dextrorphan, the 3-hydroxy derivative of dextromethorphan. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Hepatic. Rapidly and extensively metabolized to dextrorphan (active metabolite). One well known metabolic catalyst involved is a specific cytochrome P450 enzyme known as 2D6, or CYP2D6.
Half Life: 3-6 hours |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 165 mg/kg (mice) (8)
LD50: 350 mg/kg (rat) (8)
|
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | The primary use of dextromethorphan is as a cough suppressant, for the temporary relief of cough caused by minor throat and bronchial irritation (as commonly accompanies the common cold), as well as those resulting from inhaled irritants. In addition, a combination of dextromethorphan and quinidine has been shown to alleviate symptoms of easy laughing and crying (pseudobulbar affect) in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Hypertension, shallow respiration. Dextromethorphan can cause other gastrointestinal disturbances. [Wikipedia] |
|---|
| Symptoms | symptoms include vomitting, drowiness, diarrhea, urinary retention, fever, and sweating. [Wikipedia] |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00514 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB01920 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5362449 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL52440 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 4642423 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C06947 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 4470 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Dextromethorphan |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Dextromethorphan |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Mahendra R. Patel, “Sustained Release Suspension Preparation For Dextromethorphan.” U.S. Patent US20130115253, issued May 09, 2013. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Brooks BR, Thisted RA, Appel SH, Bradley WG, Olney RK, Berg JE, Pope LE, Smith RA: Treatment of pseudobulbar affect in ALS with dextromethorphan/quinidine: a randomized trial. Neurology. 2004 Oct 26;63(8):1364-70. [15505150 ]
- Olney JW, Labruyere J, Price MT: Pathological changes induced in cerebrocortical neurons by phencyclidine and related drugs. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1360-2. [2660263 ]
- Hargreaves RJ, Hill RG, Iversen LL: Neuroprotective NMDA antagonists: the controversy over their potential for adverse effects on cortical neuronal morphology. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 1994;60:15-9. [7976530 ]
- Carliss RD, Radovsky A, Chengelis CP, O'Neill TP, Shuey DL: Oral administration of dextromethorphan does not produce neuronal vacuolation in the rat brain. Neurotoxicology. 2007 Jul;28(4):813-8. Epub 2007 Apr 6. [17573115 ]
- Hernandez SC, Bertolino M, Xiao Y, Pringle KE, Caruso FS, Kellar KJ: Dextromethorphan and its metabolite dextrorphan block alpha3beta4 neuronal nicotinic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Jun;293(3):962-7. [10869398 ]
- Tang YW, Rys PN, Rutledge BJ, Mitchell PS, Smith TF, Persing DH: Comparative evaluation of colorimetric microtiter plate systems for detection of herpes simplex virus in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1998 Sep;36(9):2714-7. [9705419 ]
- Drugs.com [Link]
- IPCS Inchem monograph for Dextromethorphan [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|