Ergotamine (T3D2460)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-03 21:06:25 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:32 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D2460 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Ergotamine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Ergotamine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a vasoconstrictor found in ergot of Central Europe. It is an alpha-1 selective adrenergic agonist and is commonly used in the treatment of migraine disorders. Ergotamine acts on migraine by one of two proposed mechanisms: 1) activation of 5-HT1D receptors located on intracranial blood vessels, including those on arterio-venous anastomoses, leads to vasoconstriction, which correlates with the relief of migraine headache, and 2) activation of 5-HT1D receptors on sensory nerve endings of the trigeminal system results in the inhibition of pro-inflammatory neuropeptide release. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
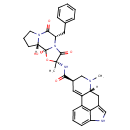
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C33H35N5O5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 581.662 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 581.264 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 113-15-5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | (4R,7R)-N-[(1S,2S,4R,7S)-7-benzyl-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-5,8-dioxo-3-oxa-6,9-diazatricyclo[7.3.0.0²,⁶]dodecan-4-yl]-6-methyl-6,11-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.0²,⁷.0¹²,¹⁶]hexadeca-1(16),2,9,12,14-pentaene-4-carboxamide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | ergomar | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H][C@@]12CCCN1C(=O)[C@]([H])(CC1=CC=CC=C1)N1C(=O)[C@@](C)(O[C@@]21O)N=C(O)[C@@]1([H])CN(C)[C@]2([H])CC3=CNC4=CC=CC(=C34)C2=C1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C33H35N5O5/c1-32(35-29(39)21-15-23-22-10-6-11-24-28(22)20(17-34-24)16-25(23)36(2)18-21)31(41)38-26(14-19-8-4-3-5-9-19)30(40)37-13-7-12-27(37)33(38,42)43-32/h3-6,8-11,15,17,21,25-27,34,42H,7,12-14,16,18H2,1-2H3,(H,35,39)/t21-,25-,26+,27+,32-,33+/m1/s1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=XCGSFFUVFURLIX-VFGNJEKYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as ergotamines, dihydroergotamines, and derivatives. These are organic compounds containing an ergotamine moiety, which is structurally characterized by a benzyl substituent attached to the piperazine ring of the ergopeptine backbone. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Alkaloids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Ergoline and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Lysergic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Ergotamines, dihydroergotamines, and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Ergomar® Sublingual Tablets are round, green tablets each containing 2 mg of ergotamine tartrate. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Oral, dermal, inhalation, and parenteral (contaminated drugs). (7) The bioavailability of sublingually administered ergotamine has not been determined. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Ergoline alkaloids tend to act as a group, producing complex and variable effects of partial agonism or antagonism at adrenergic, dopaminergic, and serotonergic receptors. Variables relating to these effects are influenced by the agent, dosage, species, tissue, physiological, and endocrinological state, and experimental conditions. In particular, ergoline alkaloids have been shown to have the significant affinity towards the 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 serotonin receptors, D1 and D2 dopamine receptors, and alpha-adrenergic receptors. This can result in a number of different effects, including vasoconstriction, convulsions, and hallucinations. Ergometrine is also known to have a non-receptor specific oxytocic activity. Ergotamine acts on migraine by one of two proposed mechanisms: 1) activation of 5-HT1D receptors located on intracranial blood vessels, including those on arterio-venous anastomoses, leading to vasoconstriction, which correlates with the relief of migraine headache, and 2) activation of 5-HT1D receptors on sensory nerve endings of the trigeminal system, resulting in the inhibition of pro-inflammatory neuropeptide release. (4, 5, 6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Ergotamine is metabolized by the liver by largely undefined pathways, and 90% of the metabolites are excreted in the bile. (1) Half Life: 2 hours | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 62 mg/kg (Intravenous, Rat) (8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | For use as therapy to abort or prevent vascular headache, e.g., migraine, migraine variants, or so called "histaminic cephalalgia". Ergotamine is a secondary metabolite (natural product) and principal alkaloid of the ergot fungus, Claviceps purpurea, and related fungi in the family Clavicipitaceae. It is used medicinally for treatment of acute migraine attacks (sometimes in combination with caffeine), and to induce childbirth and prevent post-partum haemorrhage. (12) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Vasoconstrictive complications of a serious nature may occur at times. These include ischemia, cyanosis, absence of pulse, cold extremities, gangrene, precordial distress and pain, EKG changes and muscle pains. Although these effects occur most commonly with long-term therapy at relatively high doses, they have also been reported with short-term or normal doses. Other cardiovascular adverse effects include transient tachycardia or bradycardia and hypertension. Ingestion of ergoline alkaloids is also known to cause the disease ergotism. Ergotism occurs in two forms, gangrenous and convulsive, likely depending on the different kinds and amounts of ergoline alkaloids present. (1, 9, 3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Signs of ergotamine overexposure include irritation, nausea, vomiting, headache, diarrhea, thirst, coldness of skin, pruritus, weak pulse, numbness, tingling of extremities, and confusion. Convulsive ergotism can cause painful seizures and spasms, diarrhea, paresthesias, itching, headaches, nausea and vomiting. Usually the gastrointestinal effects precede the central nervous system effects. As well as seizures there can be hallucinations and mental effects including mania or psychosis. Gangrenous ergotism causes dry gangrene as a result of vasoconstriction induced in the more poorly vascularized distal structures, such as the fingers and toes. Symptoms include desquamation, weak periphery pulse, loss of peripheral sensation, edema and ultimately the death and loss of affected tissues. (1, 10, 11) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Treatment consists of removal of the offending drug. Maintenance of adequate pulmonary ventilation, correction of hypotension, and control of convulsions and blood pressure are important considerations. Treatment of peripheral vasospasm should consist of warmth, but not heat, and protection of the ischemic limbs. Vasodilators may be beneficial but caution must be exercised to avoid aggravating an already existent hypotension. (10) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB00696 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB14834 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 8223 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL442 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 7930 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C07544 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 64318 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | D004878 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Ergotamine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Ergotamine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for ergot alkaloid derivatives, various anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs and other psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. Regulates the release of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity. May also play a role in regulating the release of other neurotransmitters. May play a role in vasoconstriction.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1D
- Uniprot ID:
- P28221
- Molecular Weight:
- 41906.38 Da
References
- Silberstein SD, McCrory DC: Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine: history, pharmacology, and efficacy. Headache. 2003 Feb;43(2):144-66. [12558771 ]
- Hoyer D, Lery H, Waeber C, Bruinvels AT, Nozulak J, Palacios JM: "5-HT1R" or 5-HT1D sites? Evidence for 5-HT1D binding sites in rabbit brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;346(3):249-54. [1407010 ]
- Lovenberg TW, Erlander MG, Baron BM, Racke M, Slone AL, Siegel BW, Craft CM, Burns JE, Danielson PE, Sutcliffe JG: Molecular cloning and functional expression of 5-HT1E-like rat and human 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2184-8. [8384716 ]
- Sanchez-Lopez A, Centurion D, Vazquez E, Arulmani U, Saxena PR, Villalon CM: Pharmacological profile of the 5-HT-induced inhibition of cardioaccelerator sympathetic outflow in pithed rats: correlation with 5-HT1 and putative 5-ht5A/5B receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Oct;140(4):725-35. Epub 2003 Sep 22. [14504136 ]
- Deliganis AV, Peroutka SJ: 5-Hydroxtryptamine1D receptor agonism predicts antimigraine efficacy. Headache. 1991 Apr;31(4):228-31. [1646776 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for ergot alkaloid derivatives, various anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs and other psychoactive substances, such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. Arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Regulates the release of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine and acetylcholine in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, nociceptive processing, pain perception, mood and behavior. Besides, plays a role in vasoconstriction of cerebral arteries.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P28222
- Molecular Weight:
- 43567.535 Da
References
- Willems EW, Trion M, De Vries P, Heiligers JP, Villalon CM, Saxena PR: Pharmacological evidence that alpha1-and alpha2-adrenoceptors mediate vasoconstriction of carotid arteriovenous anastomoses in anaesthetized pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Jul;127(5):1263-71. [10455274 ]
- Cohen ML, Schenck K: Contractile responses to sumatriptan and ergotamine in the rabbit saphenous vein: effect of selective 5-HT(1F) receptor agonists and PGF(2alpha). Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Oct;131(3):562-8. [11015308 ]
- Villalon CM, De Vries P, Rabelo G, Centurion D, Sanchez-Lopez A, Saxena P: Canine external carotid vasoconstriction to methysergide, ergotamine and dihydroergotamine: role of 5-HT1B/1D receptors and alpha2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Feb;126(3):585-94. [10188968 ]
- Valdivia LF, Centurion D, Arulmani U, Saxena PR, Villalon CM: 5-HT1B receptors, alpha2A/2C- and, to a lesser extent, alpha1-adrenoceptors mediate the external carotid vasoconstriction to ergotamine in vagosympathectomised dogs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;370(1):46-53. Epub 2004 Jun 29. [15224175 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various ergot alkaloid derivatives and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and down-stream signaling cascades and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Plays a role in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine release, 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and in the regulation of extracellular dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels, and thereby affects neural activity. May play a role in the perception of pain. Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including impulsive behavior. Required for normal proliferation of embryonic cardiac myocytes and normal heart development. Protects cardiomyocytes against apoptosis. Plays a role in the adaptation of pulmonary arteries to chronic hypoxia. Plays a role in vasoconstriction. Required for normal osteoblast function and proliferation, and for maintaining normal bone density. Required for normal proliferation of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the intestine.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2B
- Uniprot ID:
- P41595
- Molecular Weight:
- 54297.41 Da
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Bom AH, Heiligers JP, Saxena PR, Verdouw PD: Reduction of cephalic arteriovenous shunting by ergotamine is not mediated by 5-HT1-like or 5-HT2 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):383-90. [2758221 ]
- Panconesi A, Anselmi B, Curradi C, Perfetto F, Piluso A, Franchi G: Comparison between venoconstrictor effects of sumatriptan and ergotamine in migraine patients. Headache. 1994 Apr;34(4):194-7. [8014033 ]
- Rothman RB, Baumann MH, Savage JE, Rauser L, McBride A, Hufeisen SJ, Roth BL: Evidence for possible involvement of 5-HT(2B) receptors in the cardiac valvulopathy associated with fenfluramine and other serotonergic medications. Circulation. 2000 Dec 5;102(23):2836-41. [11104741 ]
- General Function:
- Protein heterodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- This alpha-adrenergic receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Its effect is mediated by G(q) and G(11) proteins. Nuclear ADRA1A-ADRA1B heterooligomers regulate phenylephrine(PE)-stimulated ERK signaling in cardiac myocytes.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P35348
- Molecular Weight:
- 51486.005 Da
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Valdivia LF, Centurion D, Arulmani U, Saxena PR, Villalon CM: 5-HT1B receptors, alpha2A/2C- and, to a lesser extent, alpha1-adrenoceptors mediate the external carotid vasoconstriction to ergotamine in vagosympathectomised dogs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;370(1):46-53. Epub 2004 Jun 29. [15224175 ]
- Gornemann T, Jahnichen S, Schurad B, Latte KP, Horowski R, Tack J, Flieger M, Pertz HH: Pharmacological properties of a wide array of ergolines at functional alpha(1)-adrenoceptor subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;376(5):321-30. Epub 2007 Dec 8. [18066532 ]
- General Function:
- Virus receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including mescaline, psilocybin, 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates phospholipase C and a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Affects neural activity, perception, cognition and mood. Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including responses to anxiogenic situations and psychoactive substances. Plays a role in intestinal smooth muscle contraction, and may play a role in arterial vasoconstriction.(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human JC polyomavirus/JCPyV.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P28223
- Molecular Weight:
- 52602.58 Da
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Bom AH, Heiligers JP, Saxena PR, Verdouw PD: Reduction of cephalic arteriovenous shunting by ergotamine is not mediated by 5-HT1-like or 5-HT2 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):383-90. [2758221 ]
- Panconesi A, Anselmi B, Curradi C, Perfetto F, Piluso A, Franchi G: Comparison between venoconstrictor effects of sumatriptan and ergotamine in migraine patients. Headache. 1994 Apr;34(4):194-7. [8014033 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including ergot alkaloid derivatives, 1-2,5,-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and down-stream signaling cascades and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Regulates neuronal activity via the activation of short transient receptor potential calcium channels in the brain, and thereby modulates the activation of pro-opiomelacortin neurons and the release of CRH that then regulates the release of corticosterone. Plays a role in the regulation of appetite and eating behavior, responses to anxiogenic stimuli and stress. Plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P28335
- Molecular Weight:
- 51820.705 Da
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Bom AH, Heiligers JP, Saxena PR, Verdouw PD: Reduction of cephalic arteriovenous shunting by ergotamine is not mediated by 5-HT1-like or 5-HT2 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):383-90. [2758221 ]
- Panconesi A, Anselmi B, Curradi C, Perfetto F, Piluso A, Franchi G: Comparison between venoconstrictor effects of sumatriptan and ergotamine in migraine patients. Headache. 1994 Apr;34(4):194-7. [8014033 ]
- General Function:
- Thioesterase binding
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is oxymetazoline > clonidine > epinephrine > norepinephrine > phenylephrine > dopamine > p-synephrine > p-tyramine > serotonin = p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > phentolamine = mianserine > chlorpromazine = spiperone = prazosin > propanolol > alprenolol = pindolol.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08913
- Molecular Weight:
- 48956.275 Da
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Valdivia LF, Centurion D, Arulmani U, Saxena PR, Villalon CM: 5-HT1B receptors, alpha2A/2C- and, to a lesser extent, alpha1-adrenoceptors mediate the external carotid vasoconstriction to ergotamine in vagosympathectomised dogs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;370(1):46-53. Epub 2004 Jun 29. [15224175 ]
- General Function:
- Epinephrine binding
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is clonidine > norepinephrine > epinephrine = oxymetazoline > dopamine > p-tyramine = phenylephrine > serotonin > p-synephrine / p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > chlorpromazine > phentolamine > mianserine > spiperone > prazosin > alprenolol > propanolol > pindolol.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2B
- Uniprot ID:
- P18089
- Molecular Weight:
- 49565.8 Da
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Valdivia LF, Centurion D, Arulmani U, Saxena PR, Villalon CM: 5-HT1B receptors, alpha2A/2C- and, to a lesser extent, alpha1-adrenoceptors mediate the external carotid vasoconstriction to ergotamine in vagosympathectomised dogs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;370(1):46-53. Epub 2004 Jun 29. [15224175 ]
- General Function:
- Protein heterodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- This alpha-adrenergic receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Its effect is mediated by G(q) and G(11) proteins. Nuclear ADRA1A-ADRA1B heterooligomers regulate phenylephrine (PE)-stimulated ERK signaling in cardiac myocytes.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P35368
- Molecular Weight:
- 56835.375 Da
References
- Valdivia LF, Centurion D, Arulmani U, Saxena PR, Villalon CM: 5-HT1B receptors, alpha2A/2C- and, to a lesser extent, alpha1-adrenoceptors mediate the external carotid vasoconstriction to ergotamine in vagosympathectomised dogs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;370(1):46-53. Epub 2004 Jun 29. [15224175 ]
- Gornemann T, Jahnichen S, Schurad B, Latte KP, Horowski R, Tack J, Flieger M, Pertz HH: Pharmacological properties of a wide array of ergolines at functional alpha(1)-adrenoceptor subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;376(5):321-30. Epub 2007 Dec 8. [18066532 ]
- General Function:
- Alpha1-adrenergic receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This alpha-adrenergic receptor mediates its effect through the influx of extracellular calcium.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA1D
- Uniprot ID:
- P25100
- Molecular Weight:
- 60462.205 Da
References
- Valdivia LF, Centurion D, Arulmani U, Saxena PR, Villalon CM: 5-HT1B receptors, alpha2A/2C- and, to a lesser extent, alpha1-adrenoceptors mediate the external carotid vasoconstriction to ergotamine in vagosympathectomised dogs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;370(1):46-53. Epub 2004 Jun 29. [15224175 ]
- Gornemann T, Jahnichen S, Schurad B, Latte KP, Horowski R, Tack J, Flieger M, Pertz HH: Pharmacological properties of a wide array of ergolines at functional alpha(1)-adrenoceptor subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;376(5):321-30. Epub 2007 Dec 8. [18066532 ]
- General Function:
- Potassium channel regulator activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14416
- Molecular Weight:
- 50618.91 Da
References
- Tfelt-Hansen P, Saxena PR, Dahlof C, Pascual J, Lainez M, Henry P, Diener H, Schoenen J, Ferrari MD, Goadsby PJ: Ergotamine in the acute treatment of migraine: a review and European consensus. Brain. 2000 Jan;123 ( Pt 1):9-18. [10611116 ]
- Verhoeff NP, Visser WH, Ferrari MD, Saxena PR, van Royen EA: Dopamine D2-receptor imaging with 123I-iodobenzamide SPECT in migraine patients abusing ergotamine: does ergotamine cross the blood brain barrier? Cephalalgia. 1993 Oct;13(5):325-9. [8242725 ]
- General Function:
- Norepinephrine:sodium symporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Amine transporter. Terminates the action of noradrenaline by its high affinity sodium-dependent reuptake into presynaptic terminals.
- Gene Name:
- SLC6A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P23975
- Molecular Weight:
- 69331.42 Da
References
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity and activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that regulates the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Plays a role in the regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release and in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism. Plays a role in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, mood and behavior. Plays a role in the response to anxiogenic stimuli.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08908
- Molecular Weight:
- 46106.335 Da
References
- Bigal ME, Tepper SJ: Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine: a review. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2003 Feb;7(1):55-62. [12525272 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various alkaloids and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1F
- Uniprot ID:
- P30939
- Molecular Weight:
- 41708.505 Da
References
- Bigal ME, Tepper SJ: Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine: a review. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2003 Feb;7(1):55-62. [12525272 ]
- General Function:
- Protein homodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P18825
- Molecular Weight:
- 49521.585 Da
References
- Valdivia LF, Centurion D, Arulmani U, Saxena PR, Villalon CM: 5-HT1B receptors, alpha2A/2C- and, to a lesser extent, alpha1-adrenoceptors mediate the external carotid vasoconstriction to ergotamine in vagosympathectomised dogs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;370(1):46-53. Epub 2004 Jun 29. [15224175 ]
16. D(1) dopamine receptor (Protein Group)
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase.
- Included Proteins:
- P21728 , P21918
References
- Bigal ME, Tepper SJ: Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine: a review. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2003 Feb;7(1):55-62. [12525272 ]